How to read earthquake updates (Shindo Sokuhou) and understanding Shindo and Magnitude

When an earthquake occurs, you can get a quick report on TV and the Internet, letting you know where the earthquake hit and how much it was.
Japan has earthquakes frequently as the land lies along the boundaries of tectonic plates. Although most earthquakes are so small that you can hardly sense them, many people pay attention to get updated with the latest information as large earthquakes sometimes occur, which may affect daily life.
If an earthquake occurs somewhere in Japan while watching TV, you will get a quick report that appears on display in a few minutes. The report is "Earthquake and Seismic Intensity Information (Shindo Sokuho 震度速報), commonly called Jishin Sokuhou (地震速報).
How to read Shindo Sokuho 震度速報 (Earthquake and Seismic Intensity Information)
The short report gives information on the occurred earthquake as follows.
例:午後「10時」頃、「関東」地方で地震がありました。
震度2:・・市、 ・・市
震度3:・・市、・・市
e.g. Occurred at "10:00PM" in "Kanto Region"
Shindo 2 at -- City, -- City
Shindo 3 at -- City, -- City
It also informs Tsunami risks, for example;
例:この地震による津波の恐れはありません。
e.g. This earthquake poses no tsunami risk.
Additionally, there will be a warning for aftershocks (Yoshin 余震).
例:余震に気をつけて下さい。倒壊の恐れのある建物には近づかないようにしてください。
e.g. Watch out for the aftershocks. Stay away from damaged buildings as they might collapse.
When reporting earthquake and seismic intensity information, the Shindo (Seismic Intensity) scale is used to measure the earthquake. Shindo consists of 10 scales that describe the size of impacts and personal perception.
Shindo 1: Little tremor that you can sense if you hold still.
Shindo 2: Most people sense a tremor. You can hardly sense it while walking.
Shindo 3: People in buildings sense the shaking and feel anxious.
Shindo 4: People quickly sense the shaking and get scared. You can feel the shaking even while walking.
Shindo 5-lower: Shaking may cause fear and disrupt public transport.
Shindo 5-upper: People can hardly walk against large shaking.
Shindo 6-lower: Unfixed furniture moves/falls over. Houses with less resistance get cracks on the wall or are seriously damaged.
Shindo 6-upper to Shindo 7: You cannot stand or even move due to massive shaking. The ground gets cracks and buildings with less-residence fall over.
The difference between Shindo (Seismic Intensity) and Magnitude
Shindo (震度 Seismic Intensity) is the scale used for measuring the degree of shaking. Magnitude (マグネチュード) indicates the class of the quake size, measured at the epicenter, which means that upper-scale magnitude does not always involve heavy shakes at places far from the epicenter in-depth/distance; in other words, people in a town right near the epicenter can feel a heavy shake even if a lower-scale earthquake occurs. When an earthquake happens, people are more concerned about the intensity of the shaking (Shindo) rather than the magnitude, as it directly impacts their daily lives, causing train delays and damaging housing. That's why the quick report provides information on seismic intensity.
The scale "Magnitude" is more frequently used in news media to offer seismological data. Magnitude is rated on the scale of M1 to M8, classed M1 - M6 as being from the weakest to middle, and M7 and over as being the strongest.
Emergency Earthquake Early Warning
Emergency Earthquake Early Warning or Kinkyu Jishin Sokuho (緊急地震速報) is a system to alarm people through media TV, radio, mobile phone, and the internet when a quake is expected to occur. When a large-scale earthquake occurs, the shake spreads in waves, generating a little time delay to reach, enabling the prediction system to work.
Emergency Earthquake Early Warning is announced about 10 seconds before the shake comes up. If you hear the alarm on TV, radio, or mobile phone, CALM DOWN take immediate action for safety.
What actions to take in 10 seconds when the quake warning is announced
- Move away from windows, fragile objects and furniture in danger of collapse
- Move away from items in danger of falling.
- Open the door to secure an evacuation route.
- If you are in an elevator, press all the buttons to stop and get out to the nearest floor.
- If you are driving, pull off the car and turn on the hazard lamp. Avoid a sudden stop for cars running behind.
For detailed, precise information on what to do if a significant earthquake occurs, check the website of the Meteorological Agency. Also, taking an earthquake drill is advisable as the quake simulation allows you to experience fear and change in awareness of disaster prevention.
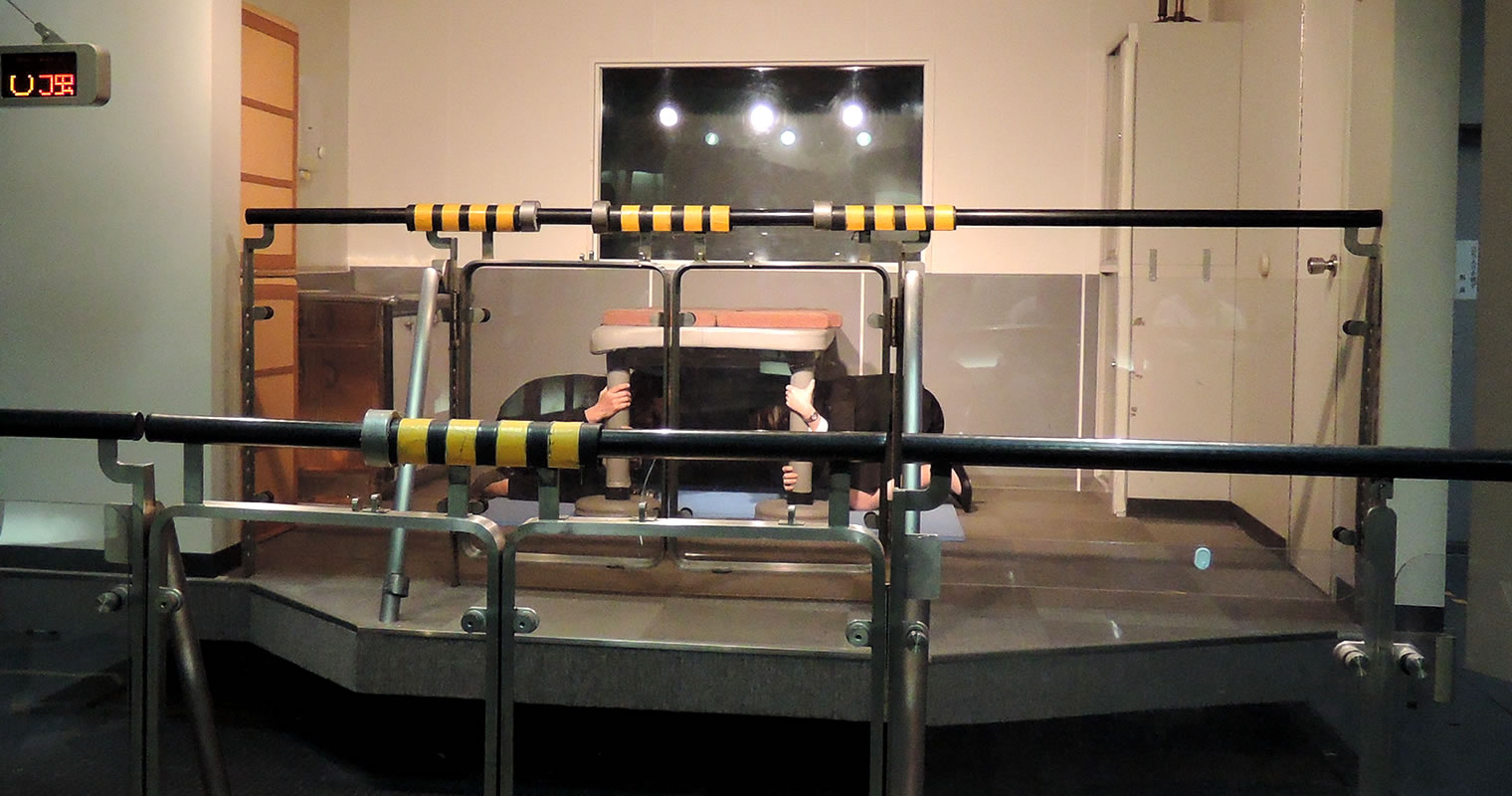
An earthquake simulation at HONJO Life Safety Learning Cente in Tokyo. At Shindo 7, you will barely withstand shock and shake.
Related Information
Earthquake Information
https://www.jma.go.jp/en/quake/
気象庁地震情報
https://www.jma.go.jp/jp/quake/
Tokyo Fire Department
https://www.tfd.metro.tokyo.lg.jp/
Desater Prevention Information by Tokyo Metropolitan Government
https://www.bousai.metro.tokyo.lg.jp/
How to Prepare and Respond to a Major Earthquake! by Tokyo Metropolitan Police Department
https://www.keishicho.metro.tokyo.lg.jp/multilingual/english/natural_disasters/respond_to_eq/
Article in Japanese:How to read Shindo Sokuhou (earthquake updates) and understanding Shindo and Magnitude